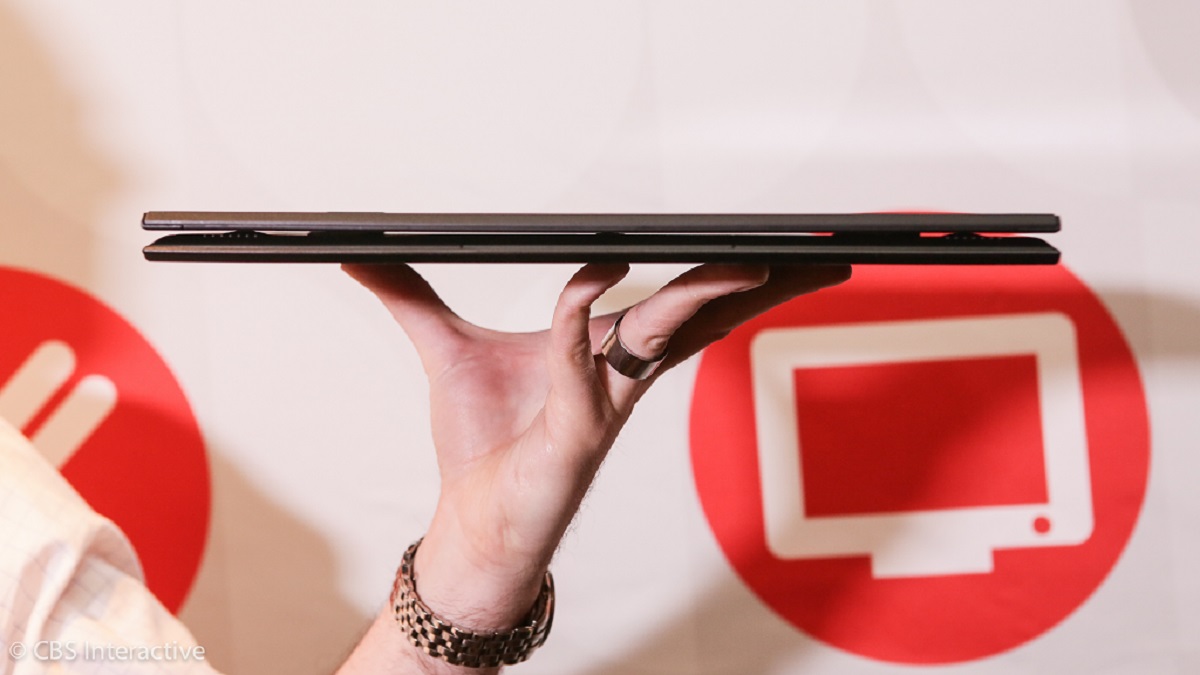
And somehow, this has all been achieved without having to compromise on performance. We’re even seeing laptops that are light enough to pick up with just two fingers, yet they come with high-end processors, displays and storage solutions. So how did we get to where we are now? Let’s look at how various laptop components have been evolving. Related Article: How To Improve Gaming Performance on Your Laptop
CPUs and Integrated Circuits
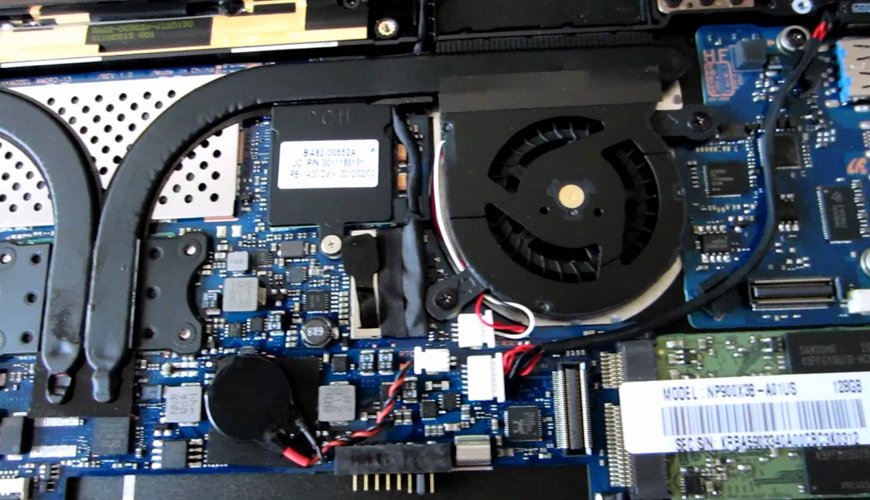
The transistors that make up a CPU are called Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor (MOSFETs). These have special physical properties that allow them to be easily scaled. Meaning that for a long time, manufacturers were able to squeeze more and more of them onto a chip hence increasing processing performance. To a point, as long as the form factor stayed about the same, these higher performance processors did not need additional electrical power. But of course, modern laptops are not lighter just because of more efficient processors. The small electronic components that supply the processor with power have also gotten smaller. They have gradually moved towards higher switching frequencies. These components include inductors and capacitors. Here’s what that means, for power to get to the CPU without frying it, the voltage has to be stepped down. Small components like inductors do this by storing small amounts of energy, stepping it down, and then releasing it to the CPU, a certain number of times every second. It turns out the physics behind this process allows higher frequency inductors to be made smaller. This contributes to savings in both weight and space in a compact device such as a laptop. Related Article: Intel is bringing 5G Windows laptops on Dell, HP, and Lenovo in 2019
Circuit Boards Boards For Laptops Are Getting Lighter
Even in printed circuit boards, the green layer that everything is mounted on has changed. The improvements here make a big difference though they are harder to see with the naked eye. Modern laptops use high density interconnects on motherboards. Meaning that copper traces go through the Printed Circuit Board (PCB) in multiple layers. This allows manufacturers to pack more connectivity into a smaller space making them lighter. Related Article: 5 Anti-theft and Recovery Measures for Laptops
Manufacturing Expertise
We’ve also seen improvements in manufacturing expertise. This comes from past experience as well as from better tools used to predict outcomes. Nowadays, manufacturers can run pretty accurate simulations on exactly how various design ideas are going to affect thermal output. That minimizes the chances of overheating in the finished product that may have been caused by bringing the components closer together.
Lighter Material and Chasis Technology for Laptops
Of course, we’d be remiss if we didn’t talk about improved materials and chassis technology. On one hand, shrinking connectors have made it so designers don’t have to use a thick design just to accommodate a gigantic printer port, for example. But there’s more to it than that, many laptops have switched to using alternative metals like lightweight magnesium alloys as you’d find in the Dragonfly Elite book from HP. Metals such as these are chosen not only for their lightweight but also for their relative strength. Meaning that they’re not just used for the outer parts but also for internal brackets that hold components in place. Manufacturing the chassis, as well as the components inside it, has also gotten more precise. There have also been advancements in techniques like CNC and injection molding. These involve heating magnesium into a slurry and then precisely injecting it into molds. That creates components of different shapes and sizes. Related Article: Laptop ports: How to identify them and what version you have
Batteries
We’ve also seen a whole-scale shift away from old-school nickel-metal hydride and nickel-cadmium batteries. These were reliable and hardy but also didn’t hold as much energy per unit of weight. At the moment, most laptop manufacturers make use of lithium-ion polymer and lithium-ion batteries. These don’t need to weigh nearly as much to hold a lot more power. They’ve existed for many years, but growing demand for lightweight devices has led to falling prices. Making them more and more common. Related Article: Why are MacBooks more expensive than Windows Laptops
Are There Trade-Offs?
Of course, there are trade-offs inherent in buying an ultra-thin laptop. They still face thermal challenges that larger machines with better airflow do not. Meaning that they can’t be shipped with the most powerful hardware available. That’s why laptops that are focused on gaming still exist and tend to be heavier and larger. But for everyday use, the lightweight and sleek portable machines that we have today are able to meet the need of the majority of users. Related Article: Some of the Best gaming Laptops for 2019