Virtualization is a technology that enables your PC to run another operating (OS) system within the same PC on top of your Windows OS. On what is generally referred to as virtual machines (VMs). It is this virtualization technology that is responsible for creating and enabling this virtual environment. With virtualization, you can create and run a whole new different computer. Or even multiple computers on a single machine. A good example is that you can install and run Windows, Ubuntu, and Linux Mint all on one PC. Virtualization is done at the hardware level where you can even create virtual disks to save data as well as create virtual switches. Also Read:
MFA vs 2FA vs 2SV: Which Authentication Method is The Best?Cloud Computing: SaaS vs PaaS vs IaaS
How is Virtualization Different From Sandbox?
Sandboxing in Windows also creates a virtual space but not virtual hardware as virtualization does. With a sandbox, you can only install and test apps and software. A key distinguishing factor is that sandboxing will not simulate a new PC environment because it will use the same hardware and drivers that your primary OS is using. And for this reason, all files and settings created for an app in a sandbox will get lost as soon as you close the sandbox or the computer. The bottom line is that a sandbox exists at the mercy of the primary operating system just like an installed software or app would. This property is what makes it a perfect platform to test apps and settings with no risk of affecting your primary operating system. On the other hand, a virtual machine behaves like a real cloned computer in that whatever changes you do inside of it remain there even if you switch to a new VM. Additionally, you cannot gain access to say VM No.1 from inside the primary OS or from inside another VM, say VM no.2. Also, VMs are not temporary platforms in that they save, store and retain all changes made even when you shut down the entire computer. This is what makes Virtualization permanent as compared to Windows Sandbox. Using a VM created by virtualization will allow you to build something, test and troubleshoot it as well as create and save files to continue working on it. Also Read:
How to tell if your laptop supports Thunderbolt 3 or USB4Why Is Your Computer Drive Smaller Than Advertised?
What Scenarios Would You Need to Use Virtualization?
There are several applications where a virtual machine would be very useful, below are a select few: I should emphasize that not all applications and software will work on a virtual machine. A good example of this is applications that majorly depend on graphics cards like games, these won’t work in a virtual environment. Also Read:
Windows Powershell vs Command PromptHow To Check Maximum RAM Capacity For Your Windows PC
What Hardware Do you Need to Enable and Use Virtualization in Windows?
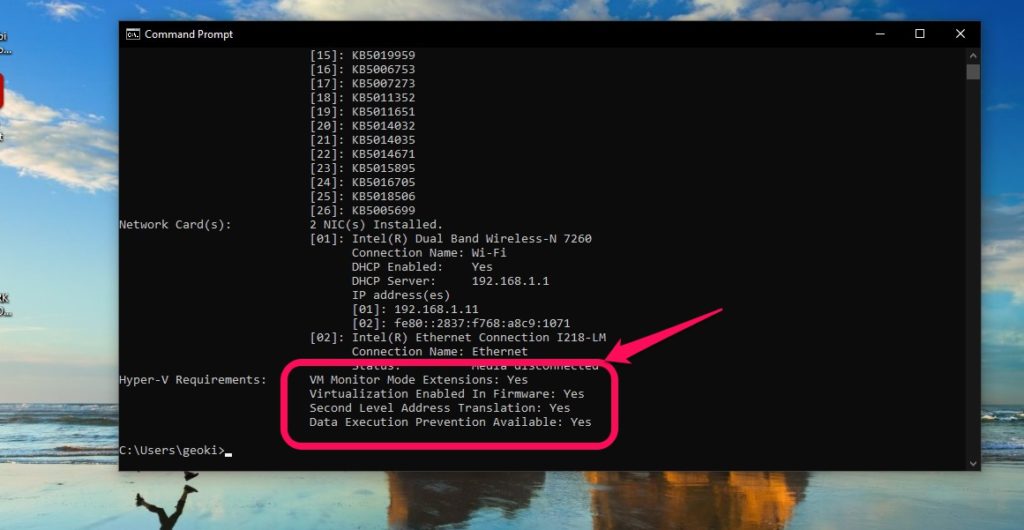
Below is a list of the minimum system requirements that you need to create and run virtual machines. Of course, it should go without saying that the more virtual environments you want to run the more robust your hardware need to be. Accessing the BIOS is quite simple on Windows 10:
Restart your PC and Press F12 when prompted during startup. You will now be presented with the boot options, here select Enter Setup and press enter. The BIOS setup screen will appear. If this does not work repeat while holding F12 instead of pressing.
Now let us confirm that your system has adequate hardware to run a virtual machine. Open CMD and type systeminfo then press enter. If everything shows Yes, you are good to go. Also Read:
Windows User Account Control (UAC) ExplainedHow TPM will make Windows 11 more secure
How to Enable Virtualization in Windows
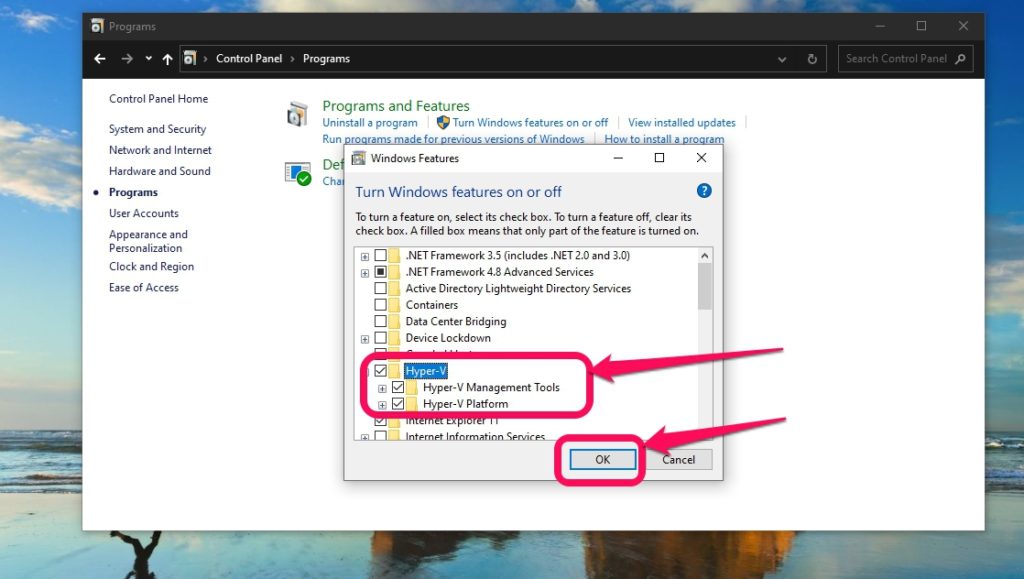
Turning on virtualization in Windows is as simple as ticking the right box and you are done. So let us find that box.
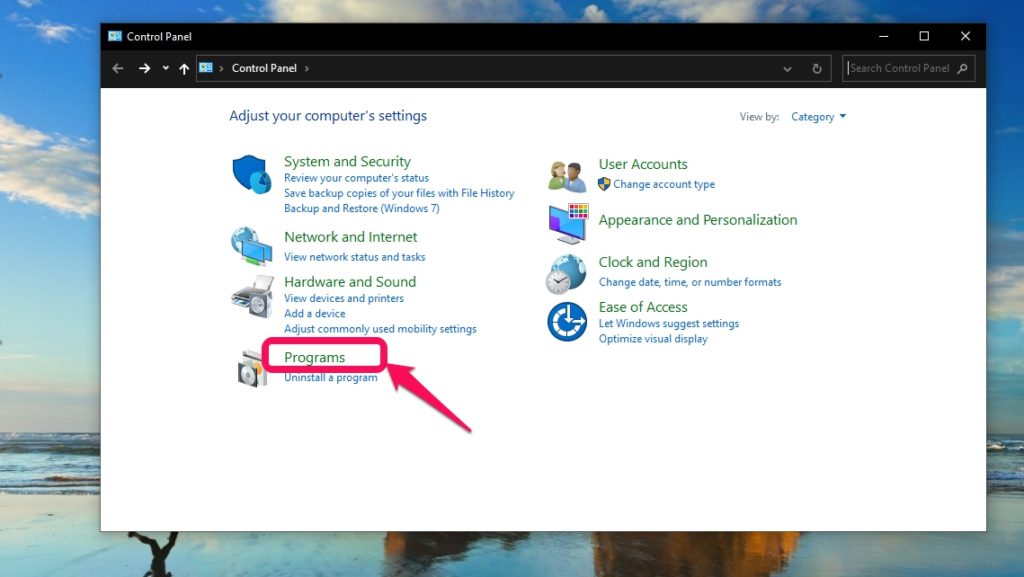
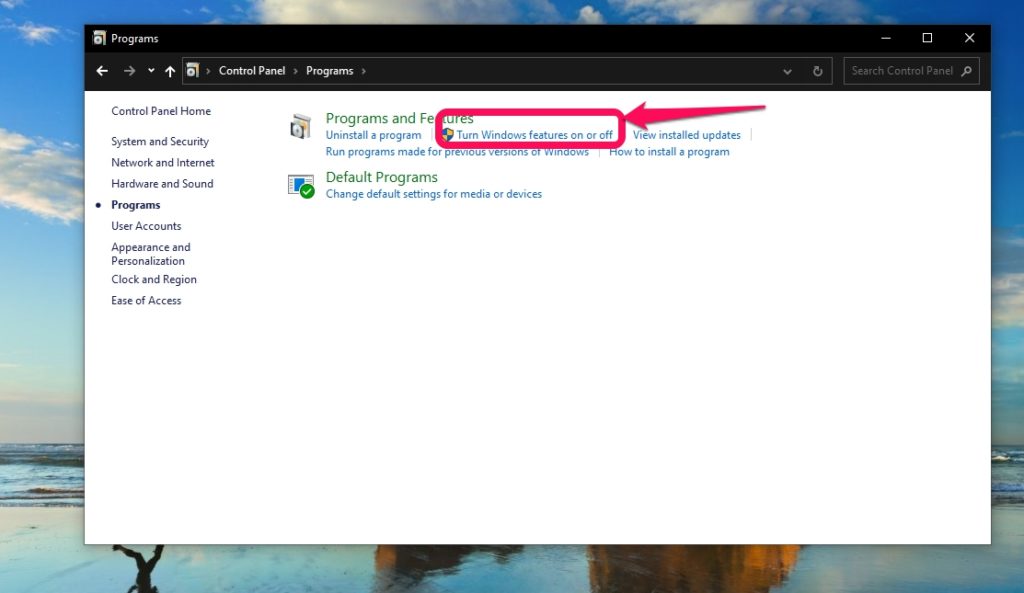
Open the Control Panel from the Windows Start Menu.Click on Programs then open Turn Windows features on or off.From the pop-up, scroll and find Hyper-V and check the box beside it and click okay. It should have two sub-folders.
The main reason why this feature is not available to Windows Home users is that it is designed to target professionals as the main users. These professionals are developers, programmers, and enthusiasts. Even though activating and using Windows Virtualization is fairly easy, and the system requirements are relatively low, I’d recommend you beef up your hardware significantly if you plan to run several virtual machines. We would like to know what you intend to use this feature for, go ahead and let us know via the comments section below. Featured Image Credit: reviewermate.com